Working with Graphs
In Akka Streams computation graphs are not expressed using a fluent DSL like linear computations are, instead they are written in a more graph-resembling DSL which aims to make translating graph drawings (e.g. from notes taken from design discussions, or illustrations in protocol specifications) to and from code simpler. In this section we'll dive into the multiple ways of constructing and re-using graphs, as well as explain common pitfalls and how to avoid them.
Graphs are needed whenever you want to perform any kind of fan-in ("multiple inputs") or fan-out ("multiple outputs") operations.
Considering linear Flows to be like roads, we can picture graph operations as junctions: multiple flows being connected at a single point.
Some graph operations which are common enough and fit the linear style of Flows, such as concat (which concatenates two
streams, such that the second one is consumed after the first one has completed), may have shorthand methods defined on
Flow or Source themselves, however you should keep in mind that those are also implemented as graph junctions.
Constructing Graphs
Graphs are built from simple Flows which serve as the linear connections within the graphs as well as junctions which serve as fan-in and fan-out points for Flows. Thanks to the junctions having meaningful types based on their behaviour and making them explicit elements these elements should be rather straightforward to use.
Akka Streams currently provide these junctions (for a detailed list see Overview of built-in stages and their semantics):
- Fan-out
Broadcast<T>– (1 input, N outputs) given an input element emits to each outputBalance<T>– (1 input, N outputs) given an input element emits to one of its output portsUnzipWith<In,A,B,...>– (1 input, N outputs) takes a function of 1 input that given a value for each input emits N output elements (where N <= 20)UnZip<A,B>– (1 input, 2 outputs) splits a stream ofPair<A,B>tuples into two streams, one of typeAand one of typeB
- Fan-in
Merge<In>– (N inputs , 1 output) picks randomly from inputs pushing them one by one to its outputMergePreferred<In>– likeMergebut if elements are available onpreferredport, it picks from it, otherwise randomly fromothersZipWith<A,B,...,Out>– (N inputs, 1 output) which takes a function of N inputs that given a value for each input emits 1 output elementZip<A,B>– (2 inputs, 1 output) is aZipWithspecialised to zipping input streams ofAandBinto aPair(A,B)tuple streamConcat<A>– (2 inputs, 1 output) concatenates two streams (first consume one, then the second one)
One of the goals of the GraphDSL DSL is to look similar to how one would draw a graph on a whiteboard, so that it is simple to translate a design from whiteboard to code and be able to relate those two. Let's illustrate this by translating the below hand drawn graph into Akka Streams:
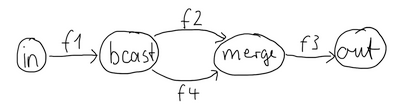
Such graph is simple to translate to the Graph DSL since each linear element corresponds to a Flow,
and each circle corresponds to either a Junction or a Source or Sink if it is beginning
or ending a Flow.
final Source<Integer, NotUsed> in = Source.from(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5));
final Sink<List<String>, CompletionStage<List<String>>> sink = Sink.head();
final Flow<Integer, Integer, NotUsed> f1 = Flow.of(Integer.class).map(elem -> elem + 10);
final Flow<Integer, Integer, NotUsed> f2 = Flow.of(Integer.class).map(elem -> elem + 20);
final Flow<Integer, String, NotUsed> f3 = Flow.of(Integer.class).map(elem -> elem.toString());
final Flow<Integer, Integer, NotUsed> f4 = Flow.of(Integer.class).map(elem -> elem + 30);
final RunnableGraph<CompletionStage<List<String>>> result =
RunnableGraph.fromGraph(
GraphDSL // create() function binds sink, out which is sink's out port and builder DSL
.create( // we need to reference out's shape in the builder DSL below (in to() function)
sink, // previously created sink (Sink)
(builder, out) -> { // variables: builder (GraphDSL.Builder) and out (SinkShape)
final UniformFanOutShape<Integer, Integer> bcast = builder.add(Broadcast.create(2));
final UniformFanInShape<Integer, Integer> merge = builder.add(Merge.create(2));
final Outlet<Integer> source = builder.add(in).out();
builder.from(source).via(builder.add(f1))
.viaFanOut(bcast).via(builder.add(f2)).viaFanIn(merge)
.via(builder.add(f3.grouped(1000))).to(out); // to() expects a SinkShape
builder.from(bcast).via(builder.add(f4)).toFanIn(merge);
return ClosedShape.getInstance();
}));
注釈
Junction reference equality defines graph node equality (i.e. the same merge instance used in a GraphDSL refers to the same location in the resulting graph).
By looking at the snippets above, it should be apparent that the builder object is mutable.
The reason for this design choice is to enable simpler creation of complex graphs, which may even contain cycles.
Once the GraphDSL has been constructed though, the RunnableGraph instance is immutable, thread-safe, and freely shareable.
The same is true of all graph pieces—sources, sinks, and flows—once they are constructed.
This means that you can safely re-use one given Flow or junction in multiple places in a processing graph.
We have seen examples of such re-use already above: the merge and broadcast junctions were imported
into the graph using builder.add(...), an operation that will make a copy of the blueprint that
is passed to it and return the inlets and outlets of the resulting copy so that they can be wired up.
Another alternative is to pass existing graphs—of any shape—into the factory method that produces a
new graph. The difference between these approaches is that importing using builder.add(...) ignores the
materialized value of the imported graph while importing via the factory method allows its inclusion;
for more details see Stream Materialization.
In the example below we prepare a graph that consists of two parallel streams,
in which we re-use the same instance of Flow, yet it will properly be
materialized as two connections between the corresponding Sources and Sinks:
final Sink<Integer, CompletionStage<Integer>> topHeadSink = Sink.head();
final Sink<Integer, CompletionStage<Integer>> bottomHeadSink = Sink.head();
final Flow<Integer, Integer, NotUsed> sharedDoubler = Flow.of(Integer.class).map(elem -> elem * 2);
final RunnableGraph<Pair<CompletionStage<Integer>, CompletionStage<Integer>>> g =
RunnableGraph.<Pair<CompletionStage<Integer>, CompletionStage<Integer>>>fromGraph(
GraphDSL.create(
topHeadSink, // import this sink into the graph
bottomHeadSink, // and this as well
Keep.both(),
(b, top, bottom) -> {
final UniformFanOutShape<Integer, Integer> bcast =
b.add(Broadcast.create(2));
b.from(b.add(Source.single(1))).viaFanOut(bcast)
.via(b.add(sharedDoubler)).to(top);
b.from(bcast).via(b.add(sharedDoubler)).to(bottom);
return ClosedShape.getInstance();
}
)
);
Constructing and combining Partial Graphs
Sometimes it is not possible (or needed) to construct the entire computation graph in one place, but instead construct all of its different phases in different places and in the end connect them all into a complete graph and run it.
This can be achieved by using the returned Graph from GraphDSL.create() rather than
passing it to RunnableGraph.fromGraph() to wrap it in a RunnableGraph.The reason of representing it as a different type is that a
RunnableGraph requires all ports to be connected, and if they are not
it will throw an exception at construction time, which helps to avoid simple
wiring errors while working with graphs. A partial graph however allows
you to return the set of yet to be connected ports from the code block that
performs the internal wiring.
Let's imagine we want to provide users with a specialized element that given 3 inputs will pick the greatest int value of each zipped triple. We'll want to expose 3 input ports (unconnected sources) and one output port (unconnected sink).
final Graph<FanInShape2<Integer, Integer, Integer>, NotUsed> zip =
ZipWith.create((Integer left, Integer right) -> Math.max(left, right));
final Graph<UniformFanInShape<Integer, Integer>, NotUsed> pickMaxOfThree =
GraphDSL.create(builder -> {
final FanInShape2<Integer, Integer, Integer> zip1 = builder.add(zip);
final FanInShape2<Integer, Integer, Integer> zip2 = builder.add(zip);
builder.from(zip1.out()).toInlet(zip2.in0());
// return the shape, which has three inputs and one output
return new UniformFanInShape<Integer, Integer>(zip2.out(),
new Inlet[] {zip1.in0(), zip1.in1(), zip2.in1()});
});
final Sink<Integer, CompletionStage<Integer>> resultSink = Sink.<Integer>head();
final RunnableGraph<CompletionStage<Integer>> g =
RunnableGraph.<CompletionStage<Integer>>fromGraph(
GraphDSL.create(resultSink, (builder, sink) -> {
// import the partial graph explicitly
final UniformFanInShape<Integer, Integer> pm = builder.add(pickMaxOfThree);
builder.from(builder.add(Source.single(1))).toInlet(pm.in(0));
builder.from(builder.add(Source.single(2))).toInlet(pm.in(1));
builder.from(builder.add(Source.single(3))).toInlet(pm.in(2));
builder.from(pm.out()).to(sink);
return ClosedShape.getInstance();
}));
final CompletionStage<Integer> max = g.run(mat);
As you can see, first we construct the partial graph that describes how to compute the maximum of two input streams, then we reuse that twice while constructing the partial graph that extends this to three input streams, then we import it (all of its nodes and connections) explicitly into the last graph in which all the undefined elements are rewired to real sources and sinks. The graph can then be run and yields the expected result.
警告
Please note that GraphDSL is not able to provide compile time type-safety about whether or not all
elements have been properly connected—this validation is performed as a runtime check during the graph's instantiation.
A partial graph also verifies that all ports are either connected or part of the returned Shape.
Constructing Sources, Sinks and Flows from Partial Graphs
Instead of treating a Graph as simply a collection of flows and junctions which may not yet all be
connected it is sometimes useful to expose such a complex graph as a simpler structure,
such as a Source, Sink or Flow.
In fact, these concepts can be easily expressed as special cases of a partially connected graph:
Sourceis a partial graph with exactly one output, that is it returns aSourceShape.Sinkis a partial graph with exactly one input, that is it returns aSinkShape.Flowis a partial graph with exactly one input and exactly one output, that is it returns aFlowShape.
Being able to hide complex graphs inside of simple elements such as Sink / Source / Flow enables you to easily create one complex element and from there on treat it as simple compound stage for linear computations.
In order to create a Source from a graph the method Source.fromGraph is used, to use it we must have a
Graph with a SourceShape. This is constructed using GraphDSL.create and providing building a SourceShape
graph. The single outlet must be provided to the SourceShape.of method and will become “the sink that must
be attached before this Source can run”.
Refer to the example below, in which we create a Source that zips together two numbers, to see this graph construction in action:
// first create an indefinite source of integer numbers
class Ints implements Iterator<Integer> {
private int next = 0;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return true;
}
@Override
public Integer next() {
return next++;
}
}
final Source<Integer, NotUsed> ints = Source.fromIterator(() -> new Ints());
final Source<Pair<Integer, Integer>, NotUsed> pairs = Source.fromGraph(
GraphDSL.create(
builder -> {
final FanInShape2<Integer, Integer, Pair<Integer, Integer>> zip =
builder.add(Zip.create());
builder.from(builder.add(ints.filter(i -> i % 2 == 0))).toInlet(zip.in0());
builder.from(builder.add(ints.filter(i -> i % 2 == 1))).toInlet(zip.in1());
return SourceShape.of(zip.out());
}));
final CompletionStage<Pair<Integer, Integer>> firstPair =
pairs.runWith(Sink.<Pair<Integer, Integer>>head(), mat);
Similarly the same can be done for a Sink<T> using SinkShape.of in which case the provided value must be an
Inlet<T>. For defining a Flow<T> we need to expose both an undefined source and sink:
final Flow<Integer, Pair<Integer, String>, NotUsed> pairs = Flow.fromGraph(GraphDSL.create(
b -> {
final UniformFanOutShape<Integer, Integer> bcast = b.add(Broadcast.create(2));
final FanInShape2<Integer, String, Pair<Integer, String>> zip =
b.add(Zip.create());
b.from(bcast).toInlet(zip.in0());
b.from(bcast).via(b.add(Flow.of(Integer.class).map(i -> i.toString()))).toInlet(zip.in1());
return FlowShape.of(bcast.in(), zip.out());
}));
Source.single(1).via(pairs).runWith(Sink.<Pair<Integer, String>>head(), mat);
Combining Sources and Sinks with simplified API
There is simplified API you can use to combine sources and sinks with junctions like: Broadcast<T>, Balance<T>,
Merge<In> and Concat<A> without the need for using the Graph DSL. The combine method takes care of constructing
the necessary graph underneath. In following example we combine two sources into one (fan-in):
Source<Integer, NotUsed> source1 = Source.single(1);
Source<Integer, NotUsed> source2 = Source.single(2);
final Source<Integer, NotUsed> sources = Source.combine(source1, source2, new ArrayList<>(),
i -> Merge.<Integer>create(i));
sources.runWith(Sink.<Integer, Integer>fold(0, (a,b) -> a + b), mat);
The same can be done for a Sink but in this case it will be fan-out:
Sink<Integer, NotUsed> sendRemotely = Sink.actorRef(actorRef, "Done");
Sink<Integer, CompletionStage<Done>> localProcessing = Sink.<Integer>foreach(a -> { /*do something useful*/ } );
Sink<Integer, NotUsed> sinks = Sink.combine(sendRemotely,localProcessing, new ArrayList<>(), a -> Broadcast.create(a));
Source.<Integer>from(Arrays.asList(new Integer[]{0, 1, 2})).runWith(sinks, mat);
Bidirectional Flows
A graph topology that is often useful is that of two flows going in opposite
directions. Take for example a codec stage that serializes outgoing messages
and deserializes incoming octet streams. Another such stage could add a framing
protocol that attaches a length header to outgoing data and parses incoming
frames back into the original octet stream chunks. These two stages are meant
to be composed, applying one atop the other as part of a protocol stack. For
this purpose exists the special type BidiFlow which is a graph that
has exactly two open inlets and two open outlets. The corresponding shape is
called BidiShape and is defined like this:
A bidirectional flow is defined just like a unidirectional Flow as
demonstrated for the codec mentioned above:
static interface Message {}
static class Ping implements Message {
final int id;
public Ping(int id) { this.id = id; }
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o instanceof Ping) {
return ((Ping) o).id == id;
} else return false;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return id;
}
}
static class Pong implements Message {
final int id;
public Pong(int id) { this.id = id; }
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o instanceof Pong) {
return ((Pong) o).id == id;
} else return false;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return id;
}
}
public static ByteString toBytes(Message msg) {
// implementation details elided ...
}
public static Message fromBytes(ByteString bytes) {
// implementation details elided ...
}
public final BidiFlow<Message, ByteString, ByteString, Message, NotUsed> codecVerbose =
BidiFlow.fromGraph(GraphDSL.create(b -> {
final FlowShape<Message, ByteString> top =
b.add(Flow.of(Message.class).map(BidiFlowDocTest::toBytes));
final FlowShape<ByteString, Message> bottom =
b.add(Flow.of(ByteString.class).map(BidiFlowDocTest::fromBytes));
return BidiShape.fromFlows(top, bottom);
}));
public final BidiFlow<Message, ByteString, ByteString, Message, NotUsed> codec =
BidiFlow.fromFunctions(BidiFlowDocTest::toBytes, BidiFlowDocTest::fromBytes);
The first version resembles the partial graph constructor, while for the simple case of a functional 1:1 transformation there is a concise convenience method as shown on the last line. The implementation of the two functions is not difficult either:
public static ByteString toBytes(Message msg) {
if (msg instanceof Ping) {
final int id = ((Ping) msg).id;
return new ByteStringBuilder().putByte((byte) 1)
.putInt(id, ByteOrder.LITTLE_ENDIAN).result();
} else {
final int id = ((Pong) msg).id;
return new ByteStringBuilder().putByte((byte) 2)
.putInt(id, ByteOrder.LITTLE_ENDIAN).result();
}
}
public static Message fromBytes(ByteString bytes) {
final ByteIterator it = bytes.iterator();
switch(it.getByte()) {
case 1:
return new Ping(it.getInt(ByteOrder.LITTLE_ENDIAN));
case 2:
return new Pong(it.getInt(ByteOrder.LITTLE_ENDIAN));
default:
throw new RuntimeException("message format error");
}
}
In this way you could easily integrate any other serialization library that turns an object into a sequence of bytes.
The other stage that we talked about is a little more involved since reversing
a framing protocol means that any received chunk of bytes may correspond to
zero or more messages. This is best implemented using a GraphStage
(see also Custom processing with GraphStage).
public static ByteString addLengthHeader(ByteString bytes) {
final int len = bytes.size();
return new ByteStringBuilder()
.putInt(len, ByteOrder.LITTLE_ENDIAN)
.append(bytes)
.result();
}
public static class FrameParser extends GraphStage<FlowShape<ByteString, ByteString>> {
public Inlet<ByteString> in = Inlet.create("FrameParser.in");
public Outlet<ByteString> out = Outlet.create("FrameParser.out");
private FlowShape<ByteString, ByteString> shape = FlowShape.of(in, out);
@Override
public FlowShape<ByteString, ByteString> shape() {
return shape;
}
@Override
public GraphStageLogic createLogic(Attributes inheritedAttributes) {
return new GraphStageLogic(shape) {
// this holds the received but not yet parsed bytes
private ByteString stash = ByteString.empty();
// this holds the current message length or -1 if at a boundary
private int needed = -1;
{
setHandler(in, new AbstractInHandler() {
@Override
public void onPush() throws Exception {
ByteString bytes = grab(in);
stash = stash.concat(bytes);
run();
}
@Override
public void onUpstreamFinish() throws Exception {
// either we are done
if (stash.isEmpty()) completeStage();
// or we still have bytes to emit
// wait with completion and let run() complete when the
// rest of the stash has been sent downstream
else if (isAvailable(out)) run();
}
});
setHandler(out, new AbstractOutHandler() {
@Override
public void onPull() throws Exception {
if (isClosed(in)) run();
else pull(in);
}
});
}
private void run() {
if (needed == -1) {
// are we at a boundary? then figure out next length
if (stash.size() < 4) {
if (isClosed(in)) completeStage();
else pull(in);
} else {
needed = stash.iterator().getInt(ByteOrder.LITTLE_ENDIAN);
stash = stash.drop(4);
run(); // cycle back to possibly already emit the next chunk
}
} else if (stash.size() < needed) {
// we are in the middle of a message, need more bytes
// or in is already closed and we cannot pull any more
if (isClosed(in)) completeStage();
else pull(in);
} else {
// we have enough to emit at least one message, so do it
final ByteString emit = stash.take(needed);
stash = stash.drop(needed);
needed = -1;
push(out, emit);
}
}
};
}
}
public final BidiFlow<ByteString, ByteString, ByteString, ByteString, NotUsed> framing =
BidiFlow.fromGraph(GraphDSL.create(b -> {
final FlowShape<ByteString, ByteString> top =
b.add(Flow.of(ByteString.class).map(BidiFlowDocTest::addLengthHeader));
final FlowShape<ByteString, ByteString> bottom =
b.add(Flow.of(ByteString.class).via(new FrameParser()));
return BidiShape.fromFlows(top, bottom);
}));
With these implementations we can build a protocol stack and test it:
/* construct protocol stack
* +------------------------------------+
* | stack |
* | |
* | +-------+ +---------+ |
* ~> O~~o | ~> | o~~O ~>
* Message | | codec | ByteString | framing | | ByteString
* <~ O~~o | <~ | o~~O <~
* | +-------+ +---------+ |
* +------------------------------------+
*/
final BidiFlow<Message, ByteString, ByteString, Message, NotUsed> stack =
codec.atop(framing);
// test it by plugging it into its own inverse and closing the right end
final Flow<Message, Message, NotUsed> pingpong =
Flow.of(Message.class).collect(new PFBuilder<Message, Message>()
.match(Ping.class, p -> new Pong(p.id))
.build()
);
final Flow<Message, Message, NotUsed> flow =
stack.atop(stack.reversed()).join(pingpong);
final CompletionStage<List<Message>> result = Source
.from(Arrays.asList(0, 1, 2))
.<Message> map(id -> new Ping(id))
.via(flow)
.grouped(10)
.runWith(Sink.<List<Message>> head(), mat);
assertArrayEquals(
new Message[] { new Pong(0), new Pong(1), new Pong(2) },
result.toCompletableFuture().get(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS).toArray(new Message[0]));
This example demonstrates how BidiFlow subgraphs can be hooked
together and also turned around with the .reversed() method. The test
simulates both parties of a network communication protocol without actually
having to open a network connection—the flows can just be connected directly.
Accessing the materialized value inside the Graph
In certain cases it might be necessary to feed back the materialized value of a Graph (partial, closed or backing a
Source, Sink, Flow or BidiFlow). This is possible by using builder.materializedValue which gives an Outlet that
can be used in the graph as an ordinary source or outlet, and which will eventually emit the materialized value.
If the materialized value is needed at more than one place, it is possible to call materializedValue any number of
times to acquire the necessary number of outlets.
final Sink<Integer, CompletionStage<Integer>> foldSink = Sink.<Integer, Integer> fold(0, (a, b) -> {
return a + b;
});
final Flow<CompletionStage<Integer>, Integer, NotUsed> flatten =
Flow.<CompletionStage<Integer>>create().mapAsync(4, x -> x);
final Flow<Integer, Integer, CompletionStage<Integer>> foldingFlow = Flow.fromGraph(
GraphDSL.create(foldSink,
(b, fold) -> {
return FlowShape.of(
fold.in(),
b.from(b.materializedValue()).via(b.add(flatten)).out());
}));
Be careful not to introduce a cycle where the materialized value actually contributes to the materialized value.
The following example demonstrates a case where the materialized CompletionStage of a fold is fed back to the fold itself.
// This cannot produce any value:
final Source<Integer, CompletionStage<Integer>> cyclicSource = Source.fromGraph(
GraphDSL.create(foldSink,
(b, fold) -> {
// - Fold cannot complete until its upstream mapAsync completes
// - mapAsync cannot complete until the materialized Future produced by
// fold completes
// As a result this Source will never emit anything, and its materialited
// Future will never complete
b.from(b.materializedValue()).via(b.add(flatten)).to(fold);
return SourceShape.of(b.from(b.materializedValue()).via(b.add(flatten)).out());
}));
Graph cycles, liveness and deadlocks
Cycles in bounded stream topologies need special considerations to avoid potential deadlocks and other liveness issues. This section shows several examples of problems that can arise from the presence of feedback arcs in stream processing graphs.
In the following examples runnable graphs are created but do not run because each have some issue and will deadlock after start.
Source variable is not defined as the nature and number of element does not matter for described problems.
The first example demonstrates a graph that contains a naive cycle.
The graph takes elements from the source, prints them, then broadcasts those elements
to a consumer (we just used Sink.ignore for now) and to a feedback arc that is merged back into the main
via a Merge junction.
// WARNING! The graph below deadlocks!
final Flow<Integer, Integer, NotUsed> printFlow =
Flow.of(Integer.class).map(s -> {
System.out.println(s);
return s;
});
RunnableGraph.fromGraph(GraphDSL.create(b -> {
final UniformFanInShape<Integer, Integer> merge = b.add(Merge.create(2));
final UniformFanOutShape<Integer, Integer> bcast = b.add(Broadcast.create(2));
final Outlet<Integer> src = b.add(source).out();
final FlowShape<Integer, Integer> printer = b.add(printFlow);
final SinkShape<Integer> ignore = b.add(Sink.ignore());
b.from(src).viaFanIn(merge).via(printer).viaFanOut(bcast).to(ignore);
b.to(merge) .fromFanOut(bcast);
return ClosedShape.getInstance();
}));
Running this we observe that after a few numbers have been printed, no more elements are logged to the console - all processing stops after some time. After some investigation we observe that:
- through merging from
sourcewe increase the number of elements flowing in the cycle - by broadcasting back to the cycle we do not decrease the number of elements in the cycle
Since Akka Streams (and Reactive Streams in general) guarantee bounded processing (see the "Buffering" section for more
details) it means that only a bounded number of elements are buffered over any time span. Since our cycle gains more and
more elements, eventually all of its internal buffers become full, backpressuring source forever. To be able
to process more elements from source elements would need to leave the cycle somehow.
If we modify our feedback loop by replacing the Merge junction with a MergePreferred we can avoid the deadlock.
MergePreferred is unfair as it always tries to consume from a preferred input port if there are elements available
before trying the other lower priority input ports. Since we feed back through the preferred port it is always guaranteed
that the elements in the cycles can flow.
// WARNING! The graph below stops consuming from "source" after a few steps
RunnableGraph.fromGraph(GraphDSL.create(b -> {
final MergePreferredShape<Integer> merge = b.add(MergePreferred.create(1));
final UniformFanOutShape<Integer, Integer> bcast = b.add(Broadcast.create(2));
final Outlet<Integer> src = b.add(source).out();
final FlowShape<Integer, Integer> printer = b.add(printFlow);
final SinkShape<Integer> ignore = b.add(Sink.ignore());
b.from(src).viaFanIn(merge).via(printer).viaFanOut(bcast).to(ignore);
b.to(merge.preferred()).fromFanOut(bcast);
return ClosedShape.getInstance();
}));
If we run the example we see that the same sequence of numbers are printed
over and over again, but the processing does not stop. Hence, we avoided the deadlock, but source is still
back-pressured forever, because buffer space is never recovered: the only action we see is the circulation of a couple
of initial elements from source.
注釈
What we see here is that in certain cases we need to choose between boundedness and liveness. Our first example would not deadlock if there would be an infinite buffer in the loop, or vice versa, if the elements in the cycle would be balanced (as many elements are removed as many are injected) then there would be no deadlock.
To make our cycle both live (not deadlocking) and fair we can introduce a dropping element on the feedback arc. In this
case we chose the buffer() operation giving it a dropping strategy OverflowStrategy.dropHead.
RunnableGraph.fromGraph(GraphDSL.create(b -> {
final UniformFanInShape<Integer, Integer> merge = b.add(Merge.create(2));
final UniformFanOutShape<Integer, Integer> bcast = b.add(Broadcast.create(2));
final FlowShape<Integer, Integer> droppyFlow = b.add(
Flow.of(Integer.class).buffer(10, OverflowStrategy.dropHead()));
final Outlet<Integer> src = b.add(source).out();
final FlowShape<Integer, Integer> printer = b.add(printFlow);
final SinkShape<Integer> ignore = b.add(Sink.ignore());
b.from(src).viaFanIn(merge).via(printer).viaFanOut(bcast).to(ignore);
b.to(merge).via(droppyFlow).fromFanOut(bcast);
return ClosedShape.getInstance();
}));
If we run this example we see that
- The flow of elements does not stop, there are always elements printed
- We see that some of the numbers are printed several times over time (due to the feedback loop) but on average the numbers are increasing in the long term
This example highlights that one solution to avoid deadlocks in the presence of potentially unbalanced cycles
(cycles where the number of circulating elements are unbounded) is to drop elements. An alternative would be to
define a larger buffer with OverflowStrategy.fail which would fail the stream instead of deadlocking it after
all buffer space has been consumed.
As we discovered in the previous examples, the core problem was the unbalanced nature of the feedback loop. We
circumvented this issue by adding a dropping element, but now we want to build a cycle that is balanced from
the beginning instead. To achieve this we modify our first graph by replacing the Merge junction with a ZipWith.
Since ZipWith takes one element from source and from the feedback arc to inject one element into the cycle,
we maintain the balance of elements.
// WARNING! The graph below never processes any elements
RunnableGraph.fromGraph(GraphDSL.create(b -> {
final FanInShape2<Integer, Integer, Integer> zip =
b.add(ZipWith.create((Integer left, Integer right) -> left));
final UniformFanOutShape<Integer, Integer> bcast = b.add(Broadcast.create(2));
final FlowShape<Integer, Integer> printer = b.add(printFlow);
final SinkShape<Integer> ignore = b.add(Sink.ignore());
b.from(b.add(source)).toInlet(zip.in0());
b.from(zip.out()).via(printer).viaFanOut(bcast).to(ignore);
b.to(zip.in1()) .fromFanOut(bcast);
return ClosedShape.getInstance();
}));
Still, when we try to run the example it turns out that no element is printed at all! After some investigation we realize that:
- In order to get the first element from
sourceinto the cycle we need an already existing element in the cycle - In order to get an initial element in the cycle we need an element from
source
These two conditions are a typical "chicken-and-egg" problem. The solution is to inject an initial
element into the cycle that is independent from source. We do this by using a Concat junction on the backwards
arc that injects a single element using Source.single.
RunnableGraph.fromGraph(GraphDSL.create(b -> {
final FanInShape2<Integer, Integer, Integer> zip =
b.add(ZipWith.create((Integer left, Integer right) -> left));
final UniformFanOutShape<Integer, Integer> bcast = b.add(Broadcast.create(2));
final UniformFanInShape<Integer, Integer> concat = b.add(Concat.create());
final FlowShape<Integer, Integer> printer = b.add(printFlow);
final SinkShape<Integer> ignore = b.add(Sink.ignore());
b.from(b.add(source)).toInlet(zip.in0());
b.from(zip.out()).via(printer).viaFanOut(bcast).to(ignore);
b.to(zip.in1()).viaFanIn(concat).from(b.add(Source.single(1)));
b.to(concat).fromFanOut(bcast);
return ClosedShape.getInstance();
}));
When we run the above example we see that processing starts and never stops. The important takeaway from this example is that balanced cycles often need an initial "kick-off" element to be injected into the cycle.
Contents